- Introduction
- GMOs and Pesticides
- Are GMOs Safe?
- Does organic means pesticide-free?
- What are the possible risks of pesticides?
- Organic food buying tips
- Why is organic food often more expensive?
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is an organism whose DNA has been modified in the laboratory in order to favor the expression of desired physiological traits or the production of desired biological products.
The effects of GMOs on health and the environment is a controversial one. In most cases, GMOs are engineered to make food crops resistant to herbicides and/or to produce an insecticide. For example, much of the sweet corn consumed in the U.S. is genetically engineered to be resistant to the herbicide Roundup and to produce its own insecticide, Bt Toxin.
GMOs are also commonly found in U.S. crops such as soybeans, alfalfa, squash, zucchini, papaya, and canola, and are present in many breakfast cereals and much of the processed food that we eat. If the ingredients on a package include corn syrup or soy lecithin, chances are it contains GMOs.
GMOs and pesticides
The use of toxic herbicides like Roundup (glyphosate) has increased 15 times since GMOs were introduced. While the World Health Organization announced that glyphosate is “probably carcinogenic to humans,” there is still some controversy over the level of health risks posed by the use of pesticides.
Are GMOs safe?
While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the biotech companies that engineer GMOs insist they are safe, many food safety advocates point out that no long term studies have ever been conducted to confirm the safety of GMO use, while some animal studies have indicated that consuming GMOs (gmo cons) may cause internal organ damage, slowed brain growth, and thickening of the digestive tract.
GMOs have been linked to increased food allergens and gastro-intestinal problems in humans. While many people think that altering the DNA of a plant or animal can increase the risk of cancer, the research has so far proven inconclusive.
Does organic mean pesticide-free?
As mentioned above, one of the primary benefits of eating organic is lower levels of pesticides. However, despite popular belief, organic farms do use pesticides. The difference is that they only use naturally-derived pesticides, rather than the synthetic pesticides used on conventional commercial farms. Natural pesticides are believed to be less toxic, however, some have been found to have health risks. That said, your exposure to harmful pesticides will likely be lower when eating organic.
What are the possible risks of pesticides?
Most of us have an accumulated build-up of pesticide exposure in our bodies due to numerous years of exposure. This chemical “body burden” as it is medically known could lead to health issues such as headaches, birth defects, and added strain on weakened immune systems.
Some studies have indicated that the use of pesticides even at low doses can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, brain tumors, breast cancer and prostate cancer.
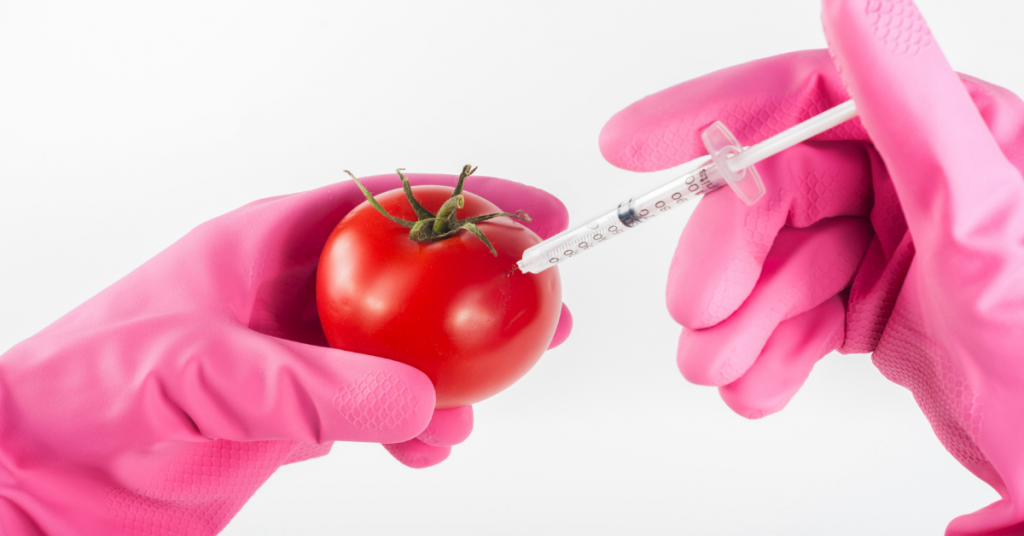
Children and fetuses are most vulnerable to pesticide exposure because their immune systems, bodies, and brains are still developing. Exposure at an early age may cause developmental delays, behavioral disorders, autism, immune system harm, and motor dysfunction.
Pregnant women are more vulnerable due to the added stress pesticides put on their already taxed organs. Plus, pesticides can be passed from mother to child in the womb, as well as through breast milk.
The widespread use of pesticides has also led to the emergence of “super weeds” and “super bugs,” which can only be killed with extremely toxic poisons like 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (a major ingredient in Agent Orange).
Organic food buying tips
Buy in season. Fruits and vegetables are cheapest and freshest when they are in season. Find out when produce is delivered to your market so you’re buying the freshest food possible.
Shop around. Compare the price of organic items at the grocery store, the farmers’ market, online, and in other venues (even the freezer aisle).
Remember that organic doesn’t always equal healthy. Making junk food sound healthy is a common marketing ploy in the food industry but organic baked goods, desserts, and snacks are usually still very high in sugar, salt, fat, or calories. It pays to read food labels carefully.
Why is organic food often more expensive?
Organic food is more labor intensive since the farmers do not use synthetic pesticides, chemical fertilizers, or drugs. Organic certification is expensive and organic feed for animals can cost twice as much. Organic farms tend to be smaller than conventional farms, which means fixed costs and overhead must be distributed across smaller produce volumes without government subsidies.

A lot of blog writers nowadays yet just a few have blog posts worth spending time on reviewing.Really thank you! Cool.